Page 101 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 101
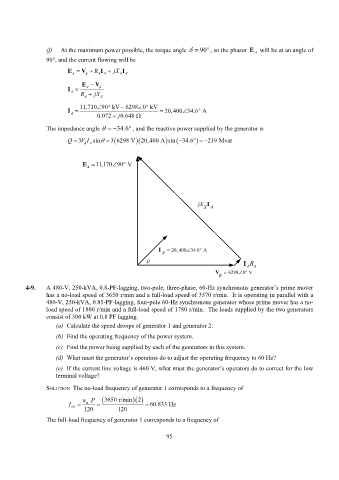
(f) At the maximum power possible, the torque angle 90, so the phasor E A will be at an angle of
90, and the current flowing will be
E V R I jX I
A A A S A
E V
I A A
R
A jX S
11,710 90 kV 6298 0 kV
I 20,400 34.6 A
A
0.072 j 0.648
The impedance angle 34.6 , and the reactive power supplied by the generator is
Q 3V I A sin 3 6298 V 20,400 A sin 34.6 219 Mvar
E A 11,170 90 V
jX I
SA
I 20, 400 34.6 A
A
I A R A
V 6298 0 V
4-9. A 480-V, 250-kVA, 0.8-PF-lagging, two-pole, three-phase, 60-Hz synchronous generator’s prime mover
has a no-load speed of 3650 r/min and a full-load speed of 3570 r/min. It is operating in parallel with a
480-V, 250-kVA, 0.85-PF-lagging, four-pole 60-Hz synchronous generator whose prime mover has a no-
load speed of 1800 r/min and a full-load speed of 1780 r/min. The loads supplied by the two generators
consist of 300 kW at 0.8 PF lagging.
(a) Calculate the speed droops of generator 1 and generator 2.
(b) Find the operating frequency of the power system.
(c) Find the power being supplied by each of the generators in this system.
(d) What must the generator’s operators do to adjust the operating frequency to 60 Hz?
(e) If the current line voltage is 460 V, what must the generator’s operators do to correct for the low
terminal voltage?
SOLUTION The no-load frequency of generator 1 corresponds to a frequency of
nP 3650 r/min 2
f m 60.833 Hz
nl1
120 120
The full-load frequency of generator 1 corresponds to a frequency of
95