Page 131 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 131
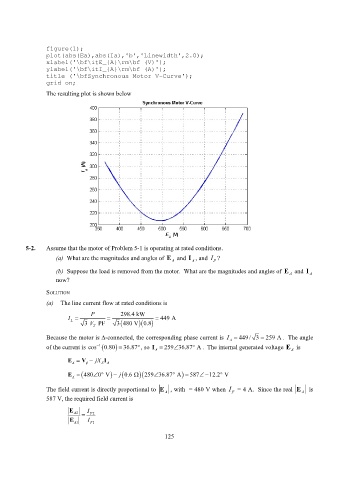
figure(1);
plot(abs(Ea),abs(Ia),'b','Linewidth',2.0);
xlabel('\bf\itE_{A}\rm\bf (V)');
ylabel('\bf\itI_{A}\rm\bf (A)');
title ('\bfSynchronous Motor V-Curve');
grid on;
The resulting plot is shown below
5-2. Assume that the motor of Problem 5-1 is operating at rated conditions.
(a) What are the magnitudes and angles of E and I A , and I ?
F
A
(b) Suppose the load is removed from the motor. What are the magnitudes and angles of E A and I
A
now?
SOLUTION
(a) The line current flow at rated conditions is
P 298.4 kW
I 449 A
L
3 V T PF 3 480 V 0.8
Because the motor is -connected, the corresponding phase current is I A 449/ 3 259 A . The angle
of the current is cos 1 0.80 36.87 , so I A 259 36.87 A . The internal generated voltage E A is
E V jX I
A S A
E 480 0 V j 0.6 259 36.87 A 587 12.2 V
A
The field current is directly proportional to E , with = 480 V when I = 4 A. Since the real E is
A
F
A
587 V, the required field current is
E A 2 I F 2
E I
A 1 F 1
125