Page 152 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 152
P 80 kW
I I 96.2 A
A ,m L ,m
3 V T PF 3 480 V 1.0
so I 96.2 0 A . This machine is Y-connected, so the phase voltage is V = 480 / 3 = 277 V.
A ,m
The internal generated voltage of the motor is
E V jX I
A ,m ,m S A ,m
E 277 0 V j 2.0 96.2 0 A
A ,m
E 337 34.8 V
A ,m
The current supplied to the motor comes from the generator, so the internal generated voltage of the
generator is
E V jX I
A ,g ,g S A ,g
E 277 0 j V 0.4 96.2 0 A
A ,g
E 280 7.9 V
A ,g
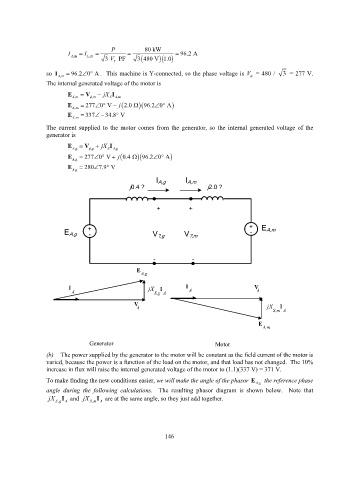
I A,g I A,m
j0.4 ? j2.0 ?
+ +
+ + E A,m
E A,g - V ?,g V ?,m -
- -
E
A,g
I jX I I V
A S,g A A
V jX I
S,m A
E
A,m
Generator Motor
(b) The power supplied by the generator to the motor will be constant as the field current of the motor is
varied, because the power is a function of the load on the motor, and that load has not changed. The 10%
increase in flux will raise the internal generated voltage of the motor to (1.1)(337 V) = 371 V.
To make finding the new conditions easier, we will make the angle of the phasor E the reference phase
, Ag
angle during the following calculations. The resulting phasor diagram is shown below. Note that
I
jX , Sg A and jX , Sm A are at the same angle, so they just add together.
I
146