Page 247 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 247
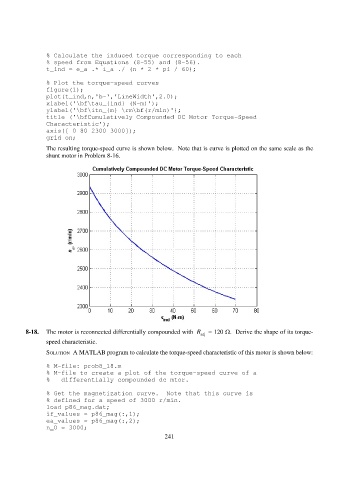
% Calculate the induced torque corresponding to each
% speed fr om Equations (8-55) and (8-56).
t_ind = e_a .* i_a ./ (n * 2 * pi / 60);
% Plot the torque-speed curves
figure(1);
pl ot(t_ind,n,'b-','LineWidth',2.0);
xlabel('\bf\tau_{ind} (N-m)');
ylabel('\bf\itn_{m} \rm\bf(r/min)');
title ('\bfCumulatively Compounded DC Moto r Torque-Speed
Ch aracteristic');
axis([ 0 80 2300 3000]);
grid on;
The resulting torque-speed curve is shown below. N ote that is curve is plotted on the same scale as the
shunt motor in Problem 8-16.
8-18. The motor is reconnected differentially compounded with R adj = 120 . Derive the shape of its torque-
speed characteristic.
SOLUTION A MATLAB program to calculate the torque-speed characteristic of this motor is shown below:
% M-file: prob8_18.m
% M-file to create a plot of the torque-speed curve of a
% differentially compounded dc mtor.
% Get the magne tization curve. Note that this curve is
% defined for a speed of 3000 r/min.
lo ad p86_mag.dat;
if_values = p86_mag(:, 1);
ea_values = p86_mag(:,2);
n_0 = 3000;
241