Page 28 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 28
SOLUTION
The first step is to apply the following identity:
1
cos cos cos cos
2
The result is
( )
pt v () () t i t 2VI cos t cos t )
1
()
pt cos 2VI t cos t t t
2
() VI
pt cos cos 2 t
Now we must apply the angle addition identity to the second term:
cos cos cos sin sin
The result is
pt cos cos2 t cos sin2 t sin
( ) VI
Collecting terms yields the final result:
p VI cos () t 1 cos2 t VI sin sin2 t
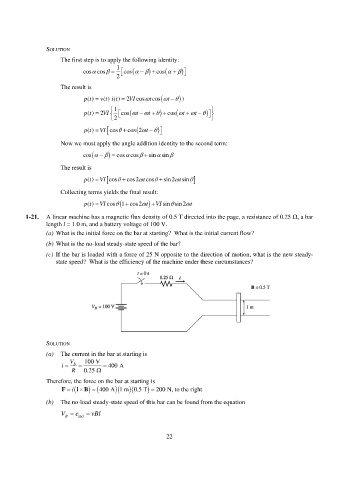
1-21. A linear machine has a magnetic flux density of 0.5 T directed into the page, a resistance of 0.25 , a bar
length l = 1.0 m, and a battery voltage of 100 V.
(a) What is the initial force on the bar at starting? What is the initial current flow?
(b) What is the no-load steady-state speed of the bar?
(c) If the bar is loaded with a force of 25 N opposite to the direction of motion, what is the new steady-
state speed? What is the efficiency of the machine under these circumstances?
SOLUTION
(a) The current in the bar at starting is
V 100 V
i B 400 A
R 0.25
Therefore, the force on the bar at starting is
F i l B 400 A 1 m 0.5 T 200 N, to the right
(b) The no-load steady-state speed of this bar can be found from the equation
V e ind vBl
B
22