Page 282 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 282
Chapter 9: Single-Phase and Special-Purpose Motors
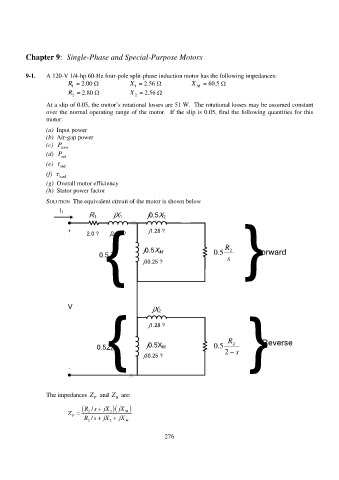
9-1. A 120-V 1/4-hp 60-Hz four-pole split-phase induction motor has the following impedances:
R 1 = 2.00 X 1 = 2.56 X M = 60.5
R 2 = 2.80 X 2 = 2.56
At a slip of 0.05, the motor’s rotational losses are 51 W. The rotational losses may be assumed constant
over the normal operating range of the motor. If the slip is 0.05, find the following quantities for this
motor:
(a) Input power
(b) Air-gap power
(c) P conv
(d) P out
(e) ind
(f) load
(g) Overall motor efficiency
(h) Stator power factor
SOLUTION The equivalent circuit of the motor is shown below
I 1
R 1 jX 1 j0.5X 2
{ j0.5X M R 2 Forward
+ j1.28 ?
2.0 ? j2.56 ?
0.5Z F j30.25 ? 5 . 0 s {
{ j1.28 ?
V jX 2
j0.5X M
0.5Z B j30.25 ? 5 . 0 2 R 2 s Reverse
- {
The impedances Z and Z are:
F
B
R s jX jX
/
Z R 2 2 / s jX 2 2 jX M
F
M
276