Page 287 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 287
i1 = v ./ ( r1 + j*x1 + 0.5*zf + 0.5*zb);
% Calculate the air-gap power
p_ag_f = abs(i1).^2 .* 0.5 .* real(zf);
p_ag_b = abs(i1).^2 .* 0.5 .* real(zb);
p_ag = p_ag_f - p_ag_b;
% Calculate torque in N-m.
t_ind = p_ag ./ w_sync;
% Plot the torque-speed curve
figure(1)
plot(nm,t_ind,'Color','b','LineWidth',2.0);
xlabel('\itn_{m} \rm(r/min)');
ylabel('\tau_{ind} \rm(N-m)');
title ('Single Phase Induction motor torque-speed
characteristic','FontSize',12);
grid on;
hold off;
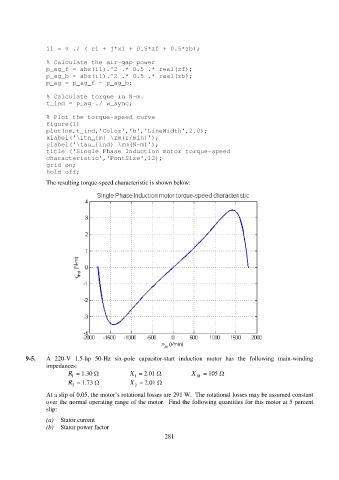
The resulting torque-speed characteristic is shown below:
9-5. A 220-V 1.5-hp 50-Hz six-pole capacitor-start induction motor has the following main-winding
impedances:
R 1 = 1.30 X 1 = 2.01 X M = 105
R 2 = 1.73 X 2 = 2.01
At a slip of 0.05, the motor’s rotational losses are 291 W. The rotational losses may be assumed constant
over the normal operating range of the motor. Find the following quantities for this motor at 5 percent
slip:
(a) Stator current
(b) Stator power factor
281