Page 117 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 117
L1644_C03.fm Page 92 Tuesday, October 21, 2003 3:11 PM
years lived disabled (YLD) and years of life lost (YOLL), while the Uniform World
Model (UWM) is based on monetization of environmental damages.
3.7.2 CULTURAL THEORY
Hofstetter (1998) proposes using the sociocultural viability theory (Thompson et al.,
1990), called cultural theory, to deal with the problem of modeling subjectivity.
Based on this theory, Goedkoop and Spriensma (1999) distinguish five extreme value
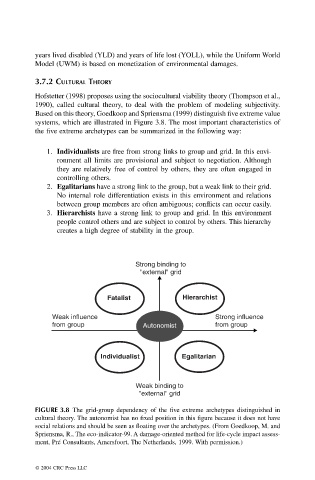
systems, which are illustrated in Figure 3.8. The most important characteristics of
the five extreme archetypes can be summarized in the following way:
1. Individualists are free from strong links to group and grid. In this envi-
ronment all limits are provisional and subject to negotiation. Although
they are relatively free of control by others, they are often engaged in
controlling others.
2. Egalitarians have a strong link to the group, but a weak link to their grid.
No internal role differentiation exists in this environment and relations
between group members are often ambiguous; conflicts can occur easily.
3. Hierarchists have a strong link to group and grid. In this environment
people control others and are subject to control by others. This hierarchy
creates a high degree of stability in the group.
Strong binding to
"external" grid
Fatalist Hierarchist
Weak influence Strong influence
from group Autonomist from group
Individualist Egalitarian
Weak binding to
"external" grid
FIGURE 3.8 The grid-group dependency of the five extreme archetypes distinguished in
cultural theory. The autonomist has no fixed position in this figure because it does not have
social relations and should be seen as floating over the archetypes. (From Goedkoop, M. and
Spriensma, R., The eco-indicator-99. A damage-oriented method for life-cycle impact assess-
ment, Pré Consultants, Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 1999. With permission.)
© 2004 CRC Press LLC