Page 191 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 191
L1644_C04.fm Page 163 Tuesday, October 21, 2003 3:13 PM
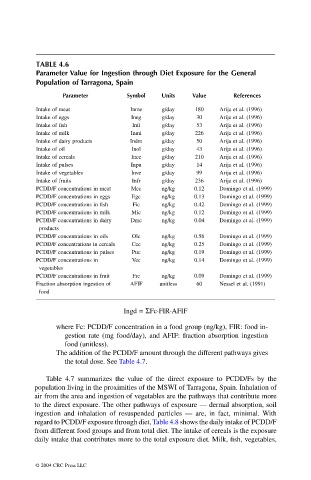
TABLE 4.6
Parameter Value for Ingestion through Diet Exposure for the General
Population of Tarragona, Spain
Parameter Symbol Units Value References
Intake of meat Inme g/day 180 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of eggs Ineg g/day 30 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of fish Infi g/day 53 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of milk Inmi g/day 226 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of dairy products Indm g/day 50 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of oil Inol g/day 43 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of cereals Ince g/day 210 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of pulses Inpu g/day 14 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of vegetables Inve g/day 99 Arija et al. (1996)
Intake of fruits Infr g/day 236 Arija et al. (1996)
PCDD/F concentrations in meat Mec ng/kg 0.12 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in eggs Egc ng/kg 0.13 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in fish Fic ng/kg 0.42 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in milk Mic ng/kg 0.12 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in dairy Dmc ng/kg 0.04 Domingo et al. (1999)
products
PCDD/F concentrations in oils Olc ng/kg 0.56 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in cereals Cec ng/kg 0.25 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in pulses Puc ng/kg 0.19 Domingo et al. (1999)
PCDD/F concentrations in Vec ng/kg 0.14 Domingo et al. (1999)
vegetables
PCDD/F concentrations in fruit Frc ng/kg 0.09 Domingo et al. (1999)
Fraction absorption ingestion of AFIF unitless 60 Nessel et al. (1991)
food
Ingd = ΣFc·FIR·AFIF
where Fc: PCDD/F concentration in a food group (ng/kg), FIR: food in-
gestion rate (mg food/day), and AFIF: fraction absorption ingestion
food (unitless).
The addition of the PCDD/F amount through the different pathways gives
the total dose. See Table 4.7.
Table 4.7 summarizes the value of the direct exposure to PCDD/Fs by the
population living in the proximities of the MSWI of Tarragona, Spain. Inhalation of
air from the area and ingestion of vegetables are the pathways that contribute more
to the direct exposure. The other pathways of exposure — dermal absorption, soil
ingestion and inhalation of resuspended particles — are, in fact, minimal. With
regard to PCDD/F exposure through diet, Table 4.8 shows the daily intake of PCDD/F
from different food groups and from total diet. The intake of cereals is the exposure
daily intake that contributes more to the total exposure diet. Milk, fish, vegetables,
© 2004 CRC Press LLC