Page 38 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 38
L1644_C01.fm Page 14 Monday, October 20, 2003 11:46 AM
3. Project 5. Factors 8. Corrective 9. Environmental
analysis identification surveillance plan
definition
submission
6. Impacts
Thematic 1. Effects Identification 7. Environmental
and geographic prevision Impacts
information evaluation
2.Environment 4. Actions 10. Public 11. Final report
definition identification evolvement submission
EVALUATION
QUALITATIVE QUANTITATIVE SIMPLIFIED
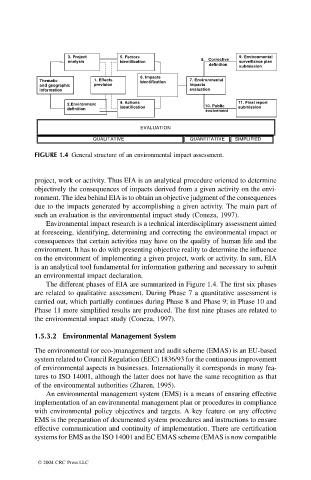
FIGURE 1.4 General structure of an environmental impact assessment.
project, work or activity. Thus EIA is an analytical procedure oriented to determine
objectively the consequences of impacts derived from a given activity on the envi-
ronment. The idea behind EIA is to obtain an objective judgment of the consequences
due to the impacts generated by accomplishing a given activity. The main part of
such an evaluation is the environmental impact study (Coneza, 1997).
Environmental impact research is a technical interdisciplinary assessment aimed
at foreseeing, identifying, determining and correcting the environmental impact or
consequences that certain activities may have on the quality of human life and the
environment. It has to do with presenting objective reality to determine the influence
on the environment of implementing a given project, work or activity. In sum, EIA
is an analytical tool fundamental for information gathering and necessary to submit
an environmental impact declaration.
The different phases of EIA are summarized in Figure 1.4. The first six phases
are related to qualitative assessment. During Phase 7 a quantitative assessment is
carried out, which partially continues during Phase 8 and Phase 9; in Phase 10 and
Phase 11 more simplified results are produced. The first nine phases are related to
the environmental impact study (Coneza, 1997).
1.5.3.2 Environmental Management System
The environmental (or eco-)management and audit scheme (EMAS) is an EU-based
system related to Council Regulation (EEC) 1836/93 for the continuous improvement
of environmental aspects in businesses. Internationally it corresponds in many fea-
tures to ISO 14001, although the latter does not have the same recognition as that
of the environmental authorities (Zharen, 1995).
An environmental management system (EMS) is a means of ensuring effective
implementation of an environmental management plan or procedures in compliance
with environmental policy objectives and targets. A key feature on any effective
EMS is the preparation of documented system procedures and instructions to ensure
effective communication and continuity of implementation. There are certification
systems for EMS as the ISO 14001 and EC EMAS scheme (EMAS is now compatible
© 2004 CRC Press LLC