Page 415 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 415
t
T h e l e e C o m p r e h e n s i v e M o d e - 1 I n e g r a t i o n o f t h e T h r e e l e e M o d e I s 393
Wireless
core network
Virtualized single cell
- _ _ _ _ - .,...
� - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - -
a
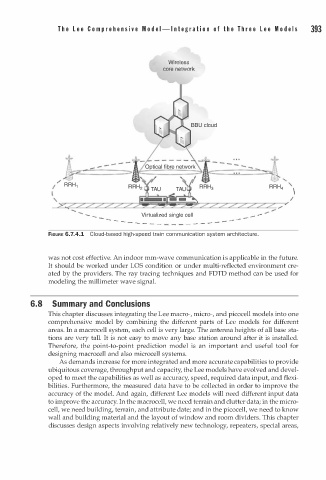
FIGURE 6.7.4.1 Cloud-based high-speed tr i n communication system architectur .
e
was not cost effective. An indoor mm-wave communication s applicable in the future.
i
It should be worked under LOS condition or under multi-reflected environment cre
ated by the providers. The ray tracing techniques and FDTD method can be used for
modeling the millimeter wave signal.
6.8 Summary and Conclusions
This chapter discusses integrating the Lee macro-, micro-, and picocell models into one
comprehensive model by combining the different parts of Lee models for different
areas. In a macrocell system, each cell is very large. The antenna heights of all base sta
tions are very tall. It is not easy to move any base station around after it is installed.
Therefore, the point-to-point prediction model is an important and useful tool for
designing macrocell and also microcell systems.
As demands increase for more integrated and more accurate capabilities to provide
ubiquitous coverage, throughput and capacity , the Lee models have evolved and devel
oped to meet the capabilities as well as accuracy, speed, required data input, and flexi
bilities. Furthermore, the measured data have to be collected in order to improve the
accuracy of the model. And again, different Lee models will need different input data
to improve the accuracy. In the macrocell, we need terrain and clutter data; in the micro
cell, we need building, terrain, and attribute date; and in the picocell, we need to know
wall and building material and the layout of window and room dividers. This chapter
discusses design aspects involving relatively new technology, repeaters, special areas,