Page 179 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 179
150 FNTELLIGENT COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
brightness g of reflective light can be regarded as an image. In this case, g can be
expressed by the following equation:
where the amount of incident light is /, and the amount of reflective light is I 0. So
in the case where the image is blackish due to an insufficient amount of reflective
light, g is bigger. When the amount of reflective light is too great, making the image
whitish, g is a small value.
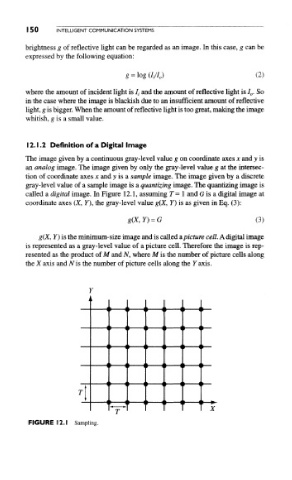
12.1.2 Definition of a Digital Image
The image given by a continuous gray-level value g on coordinate axes x and y is
an analog image. The image given by only the gray-level value g at the intersec-
tion of coordinate axes x and y is a sample image. The image given by a discrete
gray-level value of a sample image is a quantizing image. The quantizing image is
called a digital image. In Figure 12.1, assuming T-l and G is a digital image at
coordinate axes (X, F), the gray-level value g(X, Y) is as given in Eq. (3):
g(X, Y) is the minimum-size image and is called a picture cell. A digital image
is represented as a gray-level value of a picture cell. Therefore the image is rep-
resented as the product of M and N, where M is the number of picture cells along
the X axis and N is the number of picture cells along the F axis.
FIGURE 12.1 Sampling.