Page 205 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 205
CHAPTER 12 /COMPUTERVISION 175
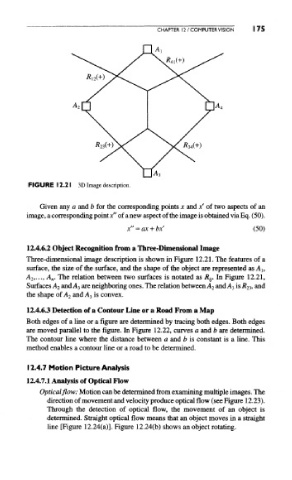
FIGURE 12.21 3D Image description.
Given any a and b for the corresponding points x and x' of two aspects of an
image, a corresponding point x" of a new aspect of the image is obtained via Eq. (50).
12.4.6.2 Object Recognition from a Three-Dimensional Image
Three-dimensional image description is shown in Figure 12.21. The features of a
surface, the size of the surface, and the shape of the object are represented as A,,
A 2,..., A n, The relation between two surfaces is notated as Ry, In Figure 12.21,
Surfaces A 2 and A 3 are neighboring ones. The relation between A 2 and A 3 is R 23, and
the shape of A 2 and A 3 is convex.
12.4.63 Detection of a Contour Line or a Road From a Map
Both edges of a line or a figure are determined by tracing bom edges. Both edges
are moved parallel to the figure. In Figure 12.22, curves a and b are determined.
The contour line where the distance between a and b is constant is a line. This
method enables a contour line or a road to be determined.
12.4.7 Motion Picture Analysis
12.4.7.1 Analysis of Optical Flow
Optical/low: Motion can be determined from examining multiple images. The
direction of movement and velocity produce optical flow (see Figure 12.23).
Through the detection of optical flow, the movement of an object is
determined. Straight optical flow means that an object moves in a straight
line [Figure 12.24(a)]. Figure 12.24(b) shows an object rotating.