Page 253 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 253
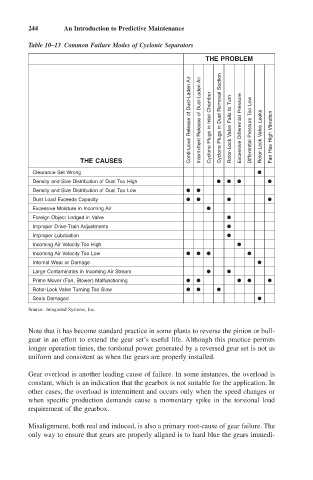
244 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
Table 10–13 Common Failure Modes of Cyclonic Separators
THE PROBLEM
Continuous Release of Dust-Laden Air Intermittent Release of Dust-Laden Air Cyclone Plugs in Inlet Chamber Cyclone Plugs in Dust Removal Section Rotor-Lock Valve Fails to Turn Excessive Differential Pressure Differential Pressure Too Low Rotor-Lock Valve Leaks Fan Has High Vibration
THE CAUSES
Clearance Set Wrong
Density and Size Distribution of Dust Too High
Density and Size Distribution of Dust Too Low
Dust Load Exceeds Capacity
Excessive Moisture in Incoming Air
Foreign Object Lodged in Valve
Improper Drive-Train Adjustments
Improper Lubrication
Incoming Air Velocity Too High
Incoming Air Velocity Too Low
Internal Wear or Damage
Large Contaminates in Incoming Air Stream
Prime Mover (Fan, Blower) Malfunctioning
Rotor-Lock Valve Turning Too Slow
Seals Damaged
Source: Integrated Systems, Inc.
Note that it has become standard practice in some plants to reverse the pinion or bull-
gear in an effort to extend the gear set’s useful life. Although this practice permits
longer operation times, the torsional power generated by a reversed gear set is not as
uniform and consistent as when the gears are properly installed.
Gear overload is another leading cause of failure. In some instances, the overload is
constant, which is an indication that the gearbox is not suitable for the application. In
other cases, the overload is intermittent and occurs only when the speed changes or
when specific production demands cause a momentary spike in the torsional load
requirement of the gearbox.
Misalignment, both real and induced, is also a primary root-cause of gear failure. The
only way to ensure that gears are properly aligned is to hard blue the gears immedi-