Page 283 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 283
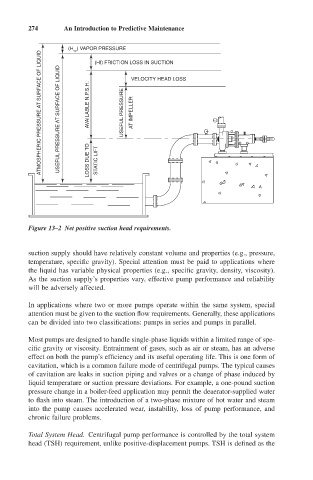
274 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
(H ) VAPOR PRESSURE VELOCITY HEAD LOSS
vp
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE AT SURFACE OF LIQUID USEFUL PRESSURE AT SURFACE OF LIQUID AVAILABLE N.P.S.H. LOSS DUE TO STATIC LIFT USEFUL PRESSURE AT IMPELLER
(Hf) FRICTION LOSS IN SUCTION
Figure 13–2 Net positive suction head requirements.
suction supply should have relatively constant volume and properties (e.g., pressure,
temperature, specific gravity). Special attention must be paid to applications where
the liquid has variable physical properties (e.g., specific gravity, density, viscosity).
As the suction supply’s properties vary, effective pump performance and reliability
will be adversely affected.
In applications where two or more pumps operate within the same system, special
attention must be given to the suction flow requirements. Generally, these applications
can be divided into two classifications: pumps in series and pumps in parallel.
Most pumps are designed to handle single-phase liquids within a limited range of spe-
cific gravity or viscosity. Entrainment of gases, such as air or steam, has an adverse
effect on both the pump’s efficiency and its useful operating life. This is one form of
cavitation, which is a common failure mode of centrifugal pumps. The typical causes
of cavitation are leaks in suction piping and valves or a change of phase induced by
liquid temperature or suction pressure deviations. For example, a one-pound suction
pressure change in a boiler-feed application may permit the deaerator-supplied water
to flash into steam. The introduction of a two-phase mixture of hot water and steam
into the pump causes accelerated wear, instability, loss of pump performance, and
chronic failure problems.
Total System Head. Centrifugal pump performance is controlled by the total system
head (TSH) requirement, unlike positive-displacement pumps. TSH is defined as the