Page 133 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 133
Introduction to Space Sciences and Spacecrafi Applications
120
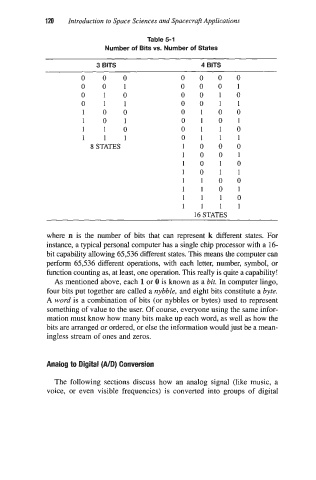
Table 5-1
Number of Bits vs. Number of States
3 BITS 4 BITS
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 1 1 0
1 1 1 0 1 1 1
8 STATES 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1
1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0
1 1 1 1
16 STATES
where n is the number of bits that can represent k different states. For
instance, a typical personal computer has a single chip processor with a 16-
bit capability allowing 65,536 different states. This means the computer can
perform 65,536 different operations, with each letter, number, symbol, or
function counting as, at least, one operation. This really is quite a capability!
As mentioned above, each 1 or 0 is known as a bit. In computer lingo,
four bits put together are called a nybble, and eight bits constitute a byte.
A word is a combination of bits (or nybbles or bytes) used to represent
something of value to the user. Of course, everyone using the same infor-
mation must know how many bits make up each word, as well as how the
bits are arranged or ordered, or else the information would just be a mean-
ingless stream of ones and zeros.
Analog to Digital (ND) Conversion
The following sections discuss how an analog signal (like music, a
voice, or even visible frequencies) is converted into groups of digital