Page 152 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 152
139
Remote Sensing
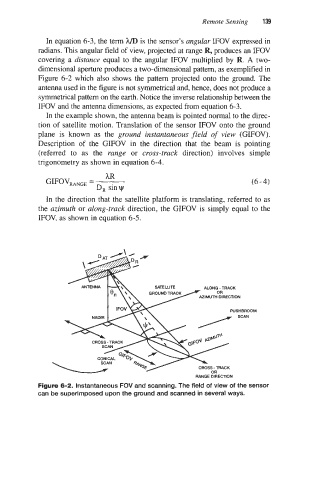
In equation 6-3, the term 3i/D is the sensor’s angular IFOV expressed in
radians. This angular field of view, projected at range R, produces an IFOV
covering a distance equal to the angular IFOV multiplied by R. A two-
dimensional aperture produces a two-dimensional pattern, as exemplified in
Figure 6-2 which also shows the pattern projected onto the ground. The
antenna used in the figure is not symmetrical and, hence, does not produce a
symmetrical pattern on the earth. Notice the inverse relationship between the
IFOV and the antenna dimensions, as expected from equation 6-3.
In the example shown, the antenna beam is pointed normal to the direc-
tion of satellite motion. Translation of the sensor IFOV onto the ground
plane is known as the ground instantaneous field of view (GIFOV).
Description of the GIFOV in the direction that the beam is pointing
(referred to as the range or cruss-truck direction) involves simple
trigonometry as shown in equation 6-4.
hR
GIFOVRANGE (6 - 4)
=
D, shy,
In the direction that the satellite platform is translating, referred to as
the azimuth or alongtruck direction, the GIFOV is simply equal to the
IFOV, as shown in equation 6-5.
IMUM DIRECTION
PUSHBROOM
RANGE DIRECTION
Figure 6-2. Instantaneous FOV and scanning. The field of view of the sensor
can be superimposed upon the ground and scanned in several ways.