Page 75 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 75
Introduction to Space Sciences and Spacecraft Applications
62
P
P
P P
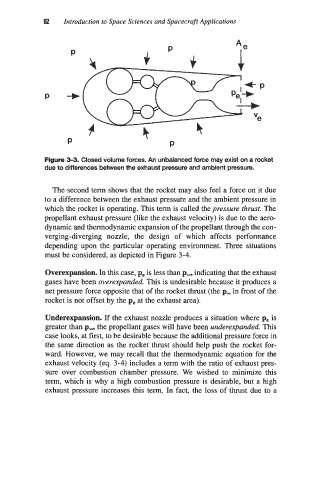
Figure 3-3. Closed volume forces. An unbalanced force may exist on a rocket
due to differences between the exhaust pmssure and ambient pressure.
The second term shows that the rocket may also feel a force on it due
to a difference between the exhaust pressure and the ambient pressure in
which the rocket is operating. This term is called the pressure thrust. The
propellant exhaust pressure (like the exhaust velocity) is due to the aero-
dynamic and thermodynamic expansion of the propellant through the con-
verging-diverging nozzle, the design of which affects performance
depending upon the particular operating environment. Three situations
must be considered, as depicted in Figure 3-4.
Overexpansion. In this case, pe is less than p-, indicating that the exhaust
gases have been overexpanded. This is undesirable because it produces a
net pressure force opposite that of the rocket thrust (the p- in front of the
rocket is not offset by the pe at the exhaust area).
Underexpansion. If the exhaust nozzle produces a situation where pe is
greater than p-, the propellant gases will have been underexpanded This
case looks, at first, to be desirable because the additional pressure force in
the same direction as the rocket thrust should help push the rocket for-
ward. However, we may recall that the thermodynamic equation for the
exhaust velocity (eq. 3-4) includes a term with the ratio of exhaust pres-
sure over combustion chamber pressure. We wished to minimize this
term, which is why a high combustion pressure is desirable, but a high
exhaust pressure increases this term. In fact, the loss of thrust due to a