Page 80 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 80
67
Propulsion
the earth rotates the launch site to another intersection with the desired
orbital plane. For some launches, such as interplanetary missions, launch
opportunities may be infrequent and launch windows may be as small as
only a few minutes. Countdowns for launches are based on completion of
all prelaunch activities before entering the launch window.
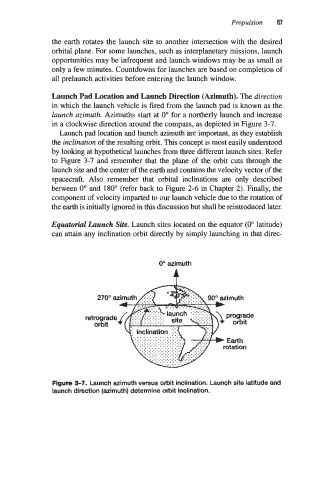
Launch Pad Location and Launch Direction (Azimuth). The direction
in which the launch vehicle is fired from the launch pad is known as the
launch azimuth. Azimuths start at 0' for a northerly launch and increase
in a clockwise direction around the compass, as depicted in Figure 3-7.
hunch pad location and launch azimuth are important, as they establish
the inclination of the resulting orbit. This concept is most easily understood
by looking at hypothetical launches from three different launch sites. Refer
to Figure 3-7 and remember that the plane of the orbit cuts through the
launch site and the center of the earth and contains the velocity vector of the
spacecraft. Also remember that orbital inclinations are only described
between 0' and 180" (refer back to Figure 2-6 in Chapter 2). Finally, the
component of velocity imparted to our launch vehicle due to the rotation of
the earth is initially ignored in this discussion but shall be reintroduced later.
Equatorial Launch Site. Launch sites located on the equator (Oo latitude)
can attain any inclination orbit directly by simply launching in that direc-
0" azimuth
.............
.............
...........
.............
..........
...........
.........
..........
Figure 3-7. Launch azimuth versus orbit inclination. Launch site latitude and
launch direction (azimuth) determine orbit inclination.