Page 360 - Intro to Tensor Calculus
P. 360
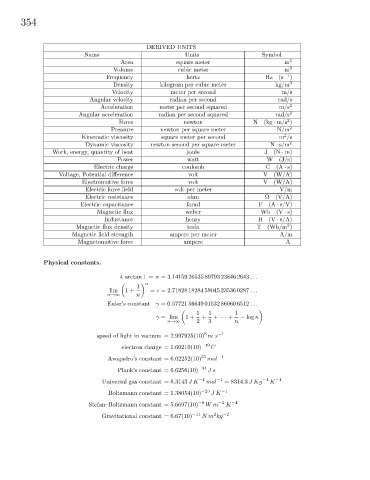
354
DERIVED UNITS
Name Units Symbol
Area square meter m 2
Volume cubic meter m 3
Frequency hertz Hz (s −1 )
Density kilogram per cubic meter kg/m 3
Velocity meter per second m/s
Angular velocity radian per second rad/s
Acceleration meter per second squared m/s 2
Angular acceleration radian per second squared rad/s 2
2
Force newton N(kg · m/s )
Pressure newton per square meter N/m 2
2
Kinematic viscosity square meter per second m /s
Dynamic viscosity newton second per square meter N · s/m 2
Work, energy, quantity of heat joule J (N · m)
Power watt W(J/s)
Electric charge coulomb C(A · s)
Voltage, Potential difference volt V(W/A)
Electromotive force volt V(W/A)
Electric force field volt per meter V/m
Electric resistance ohm Ω(V/A)
Electric capacitance farad F(A · s/V)
Magnetic flux weber Wb (V · s)
Inductance henry H(V · s/A)
2
Magnetic flux density tesla T(Wb/m )
Magnetic field strength ampere per meter A/m
Magnetomotive force ampere A
Physical constants.
4 arctan1 = π =3.14159 26535 89793 23846 2643 ...
n
1
lim 1+ = e =2.71828 18284 59045 23536 0287 ...
n→∞
n
Euler’s constant γ =0.57721 56649 01532 86060 6512 ...
1 1 1
γ = lim 1+ + + ··· + − log n
n→∞ 2 3 n
8 −1
speed of light in vacuum = 2.997925(10) ms
electron charge = 1.60210(10) −19 C
23 −1
Avogadro’s constant = 6.02252(10) mol
Plank’s constant = 6.6256(10) −34 Js
−1 −1 −1 −1
Universal gas constant = 8.3143 JK mol = 8314.3 JKg K
Boltzmann constant = 1.38054(10) −23 JK −1
Stefan–Boltzmann constant = 5.6697(10) −8 Wm −2 K −4
2
Gravitational constant = 6.67(10) −11 Nm kg −2