Page 124 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 124
4.1 Overview
build maps 107
explore
actuators
sensors
wander
avoid collisions
SENSE ACT
SENSE ACT
SENSE ACT
SENSE ACT
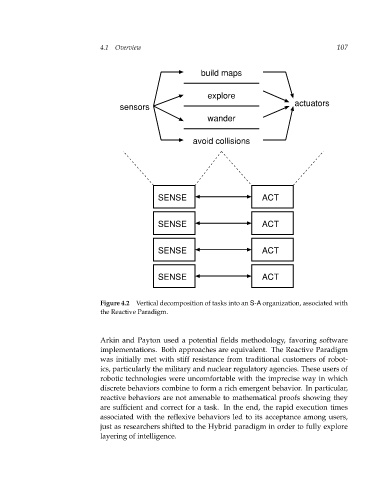
Figure 4.2 Vertical decomposition of tasks into an S-A organization, associated with
the Reactive Paradigm.
Arkin and Payton used a potential fields methodology, favoring software
implementations. Both approaches are equivalent. The Reactive Paradigm
was initially met with stiff resistance from traditional customers of robot-
ics, particularly the military and nuclear regulatory agencies. These users of
robotic technologies were uncomfortable with the imprecise way in which
discrete behaviors combine to form a rich emergent behavior. In particular,
reactive behaviors are not amenable to mathematical proofs showing they
are sufficient and correct for a task. In the end, the rapid execution times
associated with the reflexive behaviors led to its acceptance among users,
just as researchers shifted to the Hybrid paradigm in order to fully explore
layering of intelligence.