Page 63 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 63
46
2 The Hierarchical Paradigm
longer Tampa. Therefore, whenever the robot executes an operator, there
is almost always something that has to be added to the robot’s knowledge
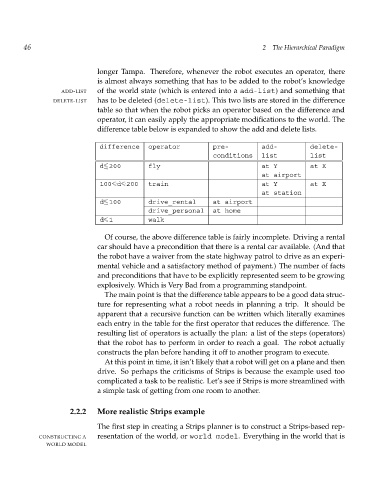
ADD-LIST of the world state (which is entered into a add-list) and something that
DELETE-LIST has to be deleted (delete-list). This two lists are stored in the difference
table so that when the robot picks an operator based on the difference and
operator, it can easily apply the appropriate modifications to the world. The
difference table below is expanded to show the add and delete lists.
difference operator pre- add- delete-
conditions list list
d 200 fly at Y at X
at airport
100<d<200 train at Y at X
at station
d 100 drive_rental at airport
drive_personal at home
d<1 walk
Of course, the above difference table is fairly incomplete. Driving a rental
car should have a precondition that there is a rental car available. (And that
the robot have a waiver from the state highway patrol to drive as an experi-
mental vehicle and a satisfactory method of payment.) The number of facts
and preconditions that have to be explicitly represented seem to be growing
explosively. Which is Very Bad from a programming standpoint.
The main point is that the difference table appears to be a good data struc-
ture for representing what a robot needs in planning a trip. It should be
apparent that a recursive function can be written which literally examines
each entry in the table for the first operator that reduces the difference. The
resulting list of operators is actually the plan: a list of the steps (operators)
that the robot has to perform in order to reach a goal. The robot actually
constructs the plan before handing it off to another program to execute.
At this point in time, it isn’t likely that a robot will get on a plane and then
drive. So perhaps the criticisms of Strips is because the example used too
complicated a task to be realistic. Let’s see if Strips is more streamlined with
a simple task of getting from one room to another.
2.2.2 More realistic Strips example
The first step in creating a Strips planner is to construct a Strips-based rep-
CONSTRUCTING A resentation of the world, or world model. Everything in the world that is
WORLD MODEL