Page 65 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 65
48
2 The Hierarchical Paradigm
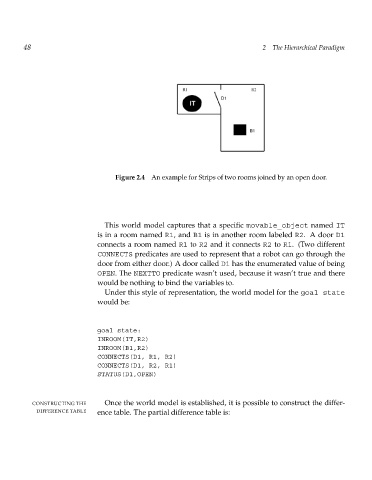
Figure 2.4 An example for Strips of two rooms joined by an open door.
This world model captures that a specific movable_object named IT
is in a room named R1,and B1 is in another room labeled R2. A door D1
connects a room named R1 to R2 and it connects R2 to R1.(Two different
CONNECTS predicates are used to represent that a robot can go through the
door from either door.) A door called D1 has the enumerated value of being
OPEN.The NEXTTO predicate wasn’t used, because it wasn’t true and there
would be nothing to bind the variables to.
Under this style of representation, the world model for the goal state
would be:
goal state:
INROOM(IT,R2)
INROOM(B1,R2)
CONNECTS(D1, R1, R2)
CONNECTS(D1, R2, R1)
STATUS(D1,OPEN)
CONSTRUCTING THE Once the world model is established, it is possible to construct the differ-
DIFFERENCE TABLE ence table. The partial difference table is: