Page 117 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 117
102
GPS Chapter 4
satellites
monitor
stations
users master
stations
uploading
station
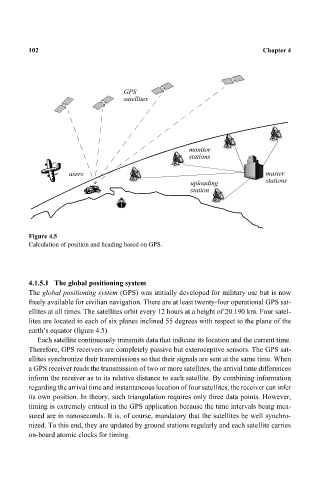
Figure 4.5
Calculation of position and heading based on GPS.
4.1.5.1 The global positioning system
The global positioning system (GPS) was initially developed for military use but is now
freely available for civilian navigation. There are at least twenty-four operational GPS sat-
ellites at all times. The satellites orbit every 12 hours at a height of 20.190 km. Four satel-
lites are located in each of six planes inclined 55 degrees with respect to the plane of the
earth’s equator (figure 4.5).
Each satellite continuously transmits data that indicate its location and the current time.
Therefore, GPS receivers are completely passive but exteroceptive sensors. The GPS sat-
ellites synchronize their transmissions so that their signals are sent at the same time. When
a GPS receiver reads the transmission of two or more satellites, the arrival time differences
inform the receiver as to its relative distance to each satellite. By combining information
regarding the arrival time and instantaneous location of four satellites, the receiver can infer
its own position. In theory, such triangulation requires only three data points. However,
timing is extremely critical in the GPS application because the time intervals being mea-
sured are in nanoseconds. It is, of course, mandatory that the satellites be well synchro-
nized. To this end, they are updated by ground stations regularly and each satellite carries
on-board atomic clocks for timing.