Page 50 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 50
Locomotion
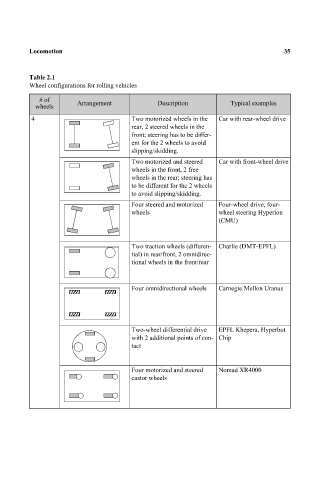
Table 2.1 35
Wheel configurations for rolling vehicles
# of Arrangement Description Typical examples
wheels
4 Two motorized wheels in the Car with rear-wheel drive
rear, 2 steered wheels in the
front; steering has to be differ-
ent for the 2 wheels to avoid
slipping/skidding.
Two motorized and steered Car with front-wheel drive
wheels in the front, 2 free
wheels in the rear; steering has
to be different for the 2 wheels
to avoid slipping/skidding.
Four steered and motorized Four-wheel drive, four-
wheels wheel steering Hyperion
(CMU)
Two traction wheels (differen- Charlie (DMT-EPFL)
tial) in rear/front, 2 omnidirec-
tional wheels in the front/rear
Four omnidirectional wheels Carnegie Mellon Uranus
Two-wheel differential drive EPFL Khepera, Hyperbot
with 2 additional points of con- Chip
tact
Four motorized and steered Nomad XR4000
castor wheels