Page 51 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 51
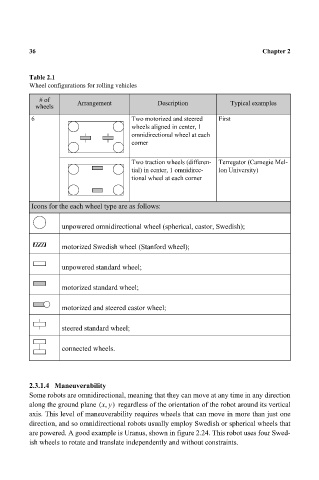
36
Table 2.1 Chapter 2
Wheel configurations for rolling vehicles
# of Arrangement Description Typical examples
wheels
6 Two motorized and steered First
wheels aligned in center, 1
omnidirectional wheel at each
corner
Two traction wheels (differen- Terregator (Carnegie Mel-
tial) in center, 1 omnidirec- lon University)
tional wheel at each corner
Icons for the each wheel type are as follows:
unpowered omnidirectional wheel (spherical, castor, Swedish);
motorized Swedish wheel (Stanford wheel);
unpowered standard wheel;
motorized standard wheel;
motorized and steered castor wheel;
steered standard wheel;
connected wheels.
2.3.1.4 Maneuverability
Some robots are omnidirectional, meaning that they can move at any time in any direction
along the ground plane xy,( ) regardless of the orientation of the robot around its vertical
axis. This level of maneuverability requires wheels that can move in more than just one
direction, and so omnidirectional robots usually employ Swedish or spherical wheels that
are powered. A good example is Uranus, shown in figure 2.24. This robot uses four Swed-
ish wheels to rotate and translate independently and without constraints.