Page 157 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 157
146 The solid-gas interface
are studied on the basis that they will remain intact when the
adsorptive has been pumped away.
Consider the diffraction from a one-dimensional row of regularly
spaced atoms. From Figure 5.19 it can be seen that the condition for
constructive interference is
A = d sin 0 = nX (5.16)
The diffracted maxima will, therefore, lie on the surfaces of cones, as
illustrated in Figure 5.20.
Diffraction from the rows of atoms in the second direction will be
similar and the diffraction maxima for the two-dimensional net will
be an array of points corresponding to the lines where the maxima
cones for each dimension meet. From equation (5.16) it can be seen
that the spacings between diffraction maxima are inversely propor-
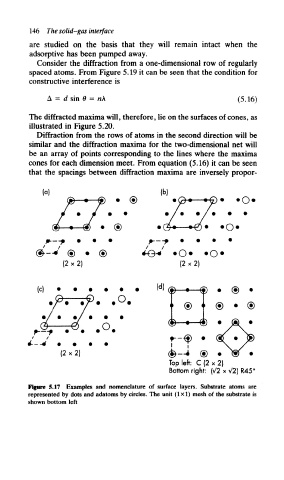
( 2 x 2 ) (2x2)
(d)
<$• €)
(£•
(2x2)
Top left: C ( 2 x 2 )
Bottom right: (v7 x V2) R45 C
Figure 5.17 Examples and nomenclature of surface layers. Substrate atoms are
represented by dots and adatoms by circles. The unit (1x1) mesh of the substrate is
shown bottom left