Page 159 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 159
148 The solid-gas interface
Incident
beam
Line of
scatterers
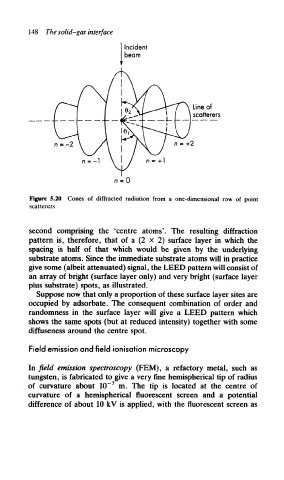
Figure 5.20 Cones of diffracted radiation from a one-dimensional row of point
scatterers
second comprising the 'centre atoms'. The resulting diffraction
pattern is, therefore, that of a (2 x 2) surface layer in which the
spacing is half of that which would be given by the underlying
substrate atoms. Since the immediate substrate atoms will in practice
give some (albeit attenuated) signal, the LEED pattern will consist of
an array of bright (surface layer only) and very bright (surface layer
plus substrate) spots, as illustrated.
Suppose now that only a proportion of these surface layer sites are
occupied by adsorbate. The consequent combination of order and
randomness in the surface layer will give a LEED pattern which
shows the same spots (but at reduced intensity) together with some
diffuseness around the centre spot.
Field emission and field ionisation microscopy
In field emission spectroscopy (FEM), a refactory metal, such as
tungsten, is fabricated to give a very fine hemispherical tip of radius
of curvature about 10~ 7 m. The tip is located at the centre of
curvature of a hemispherical fluorescent screen and a potential
difference of about 10 kV is applied, with the fluorescent screen as