Page 50 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 50
40 Kinetic properties
the solute with respect to solvation, etc., which was used in
establishing the concentration of the solution. For polydispersed
systems a number average is measured.
Measurement of osmotic pressure
A great deal of work has been devoted to the preparation of suitable
semipermeable membranes and to perfecting sensitive methods for
33 34
measuring osmotic pressure ' .
Certain practical difficulties arise if the solution is simply allowed
to rise and seek its own equilibrium level:
1. If the liquid rises up a narrow tube and the total volume of
solution is large, the liquid level may be too sensitive to
temperature fluctuations during the course of the experiment to
permit reliable measurements. In addition, a capillary rise
correction must be made under these conditions. To overcome the
difficulty associated with a sticking meniscus, which is often
encountered in the study of aqueous solutions, a liquid of low
surface tension and good wetting properties, such as toluene or
petrol ether, is used in the capillary.
(1)
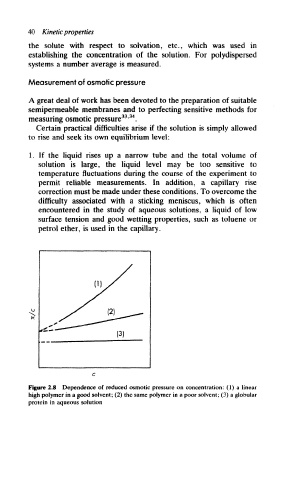
Figure 2.8 Dependence of reduced osmotic pressure on concentration: (1) a linear
high polymer in a good solvent; (2) the same polymer in a poor solvent; (3) a globular
protein in aqueous solution