Page 53 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 53
Kinetic properties 43
(2)
1
initial Na + -b
concentrations Pr- Io | a- -b
!
4
No "" a + x I Na*- b-x
Equilibrium Pr- - a 1 a- » b-x
concentrations
a- -x i
I
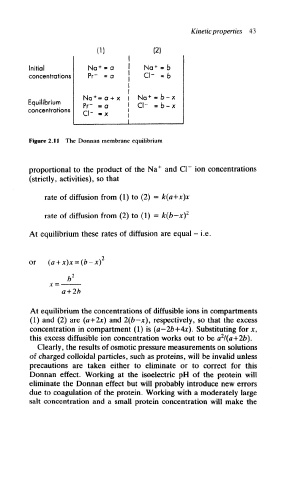
Figure 2.11 The Donnan membrane equilibrium
proportional to the product of the Na + and CI~ ion concentrations
(strictly, activities), so that
rate of diffusion from (1) to (2) = k(a+x)x
rate of diffusion from (2) to (1) = k(b-x) 2
At equilibrium these rates of diffusion are equal - i.e.
or (a + x)x-(b-x)
, 2
X ~ •
a + 2b
At equilibrium the concentrations of diffusible ions in compartments
(1) and (2) are («+2jt) and 2(b-x), respectively, so that the excess
concentration in compartment (1) is (a-26+4*). Substituting for x,
2
this excess diffusible ion concentration works out to be a l(a+2b).
Clearly, the results of osmotic pressure measurements on solutions
of charged colloidal particles, such as proteins, will be invalid unless
precautions are taken either to eliminate or to correct for this
Donnan effect. Working at the isoelectric pH of the protein will
eliminate the Donnan effect but will probably introduce new errors
due to coagulation of the protein. Working with a moderately large
salt concentration and a small protein concentration will make the