Page 247 - Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
P. 247
P1: IBE
CB908/Date
0 521 85326 5
0521853265c07
226
PHASE CHANGE
h l May 25, 2005 11:14
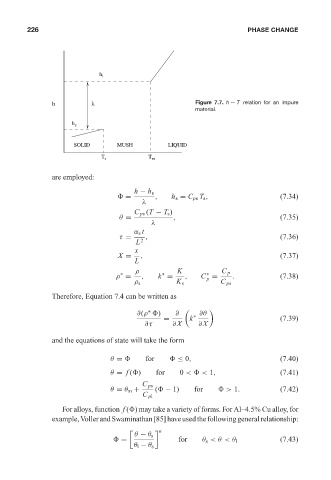
h λ Figure 7.7. h ∼ T relation for an impure
material.
h s
SOLID MUSH LIQUID
T s T m
are employed:
h − h s
= , h s = C ps T s , (7.34)
λ
C ps (T − T s )
θ = , (7.35)
λ
α s t
τ = , (7.36)
L 2
x
X = , (7.37)
L
ρ K C p
∗ ∗ ∗
ρ = , k = , C = . (7.38)
p
ρ s K s C ps
Therefore, Equation 7.4 can be written as
∗
∂(ρ ) ∂ ∂θ
= k ∗ (7.39)
∂τ ∂ X ∂ X
and the equations of state will take the form
θ = for ≤ 0, (7.40)
θ = f ( ) for 0 < < 1, (7.41)
C ps
θ = θ m + ( − 1) for > 1. (7.42)
C pl
For alloys, function f ( ) may take a variety of forms. For Al–4.5% Cu alloy, for
example,VollerandSwaminathan[85]haveusedthefollowinggeneralrelationship:
n
θ − θ s
= for θ s <θ <θ l (7.43)
θ l − θ s