Page 203 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 203
186 6 Mobile Commerce and the Internet of Things
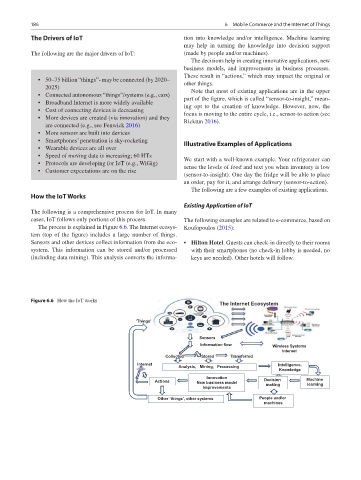
The Drivers of IoT tion into knowledge and/or intelligence. Machine learning
may help in turning the knowledge into decision support
The following are the major drivers of IoT: (made by people and/or machines).
The decisions help in creating innovative applications, new
business models, and improvements in business processes.
These result in “actions,” which may impact the original or
• 50–75 billion “things”- may be connected (by 2020–
other things.
2025) Note that most of existing applications are in the upper
• Connected autonomous “things”/systems (e.g., cars)
part of the figure, which is called “sensor-to-insight,” mean-
• Broadband Internet is more widely available ing opt to the creation of knowledge. However, now, the
• Cost of connecting devices is decreasing
focus is moving to the entire cycle, i.e., sensor-to-action (see
• More devices are created (via innovation) and they Ricktun 2016).
are connected (e.g., see Fenwick 2016)
• More sensors are built into devices
• Smartphones’ penetration is sky-rocketing Illustrative Examples of Applications
• Wearable devices are all over
• Speed of moving data is increasing; 60 HTz
We start with a well-known example. Your refrigerator can
• Protocols are developing for IoT (e.g., WiGig) sense the levels of food and text you when inventory is low
• Customer expectations are on the rise
(sensor-to-insight). One day the fridge will be able to place
an order, pay for it, and arrange delivery (sensor-to-action).
The following are a few examples of existing applications.
How the IoT Works
Existing Application of IoT
The following is a comprehensive process for IoT. In many
cases, IoT follows only portions of this process. The following examples are related to e-commerce, based on
The process is explained in Figure 6.6. The Internet ecosys- Koufopoulos (2015):
tem (top of the figure) includes a large number of things.
Sensors and other devices collect information from the eco- • Hilton Hotel. Guests can check-in directly to their rooms
system. This information can be stored and/or processed with their smartphones (no check-in lobby is needed, no
(including data mining). This analysis converts the informa- keys are needed). Other hotels will follow.
Figure 6.6 How the IoT works
The Internet Ecosystem
‘Things’
Sensors
Information flow Wireless Systems
Internet
Collected Stored Transferred
Internet Intelligence,
Analysis, Mining, Processing
Knowledge
Innovation Machine
Actions New business model Decision learning
making
Improvements
Other ‘things’, other systems People and/or
machines