Page 329 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 329
316 10 E-Commerce Security and Fraud Issues and Protections
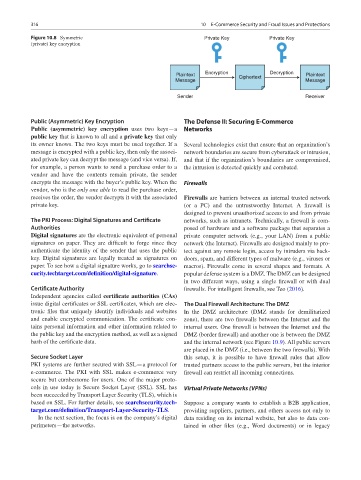
Figure 10.8 Symmetric Private Key Private Key
(private) key encryption
Plaintext Encryption Ciphertext Decryption Plaintext
Message Message
Sender Receiver
Public (Asymmetric) Key Encryption The Defense II: Securing E-Commerce
Public (asymmetric) key encryption uses two keys—a Networks
public key that is known to all and a private key that only
its owner knows. The two keys must be used together. If a Several technologies exist that ensure that an organization’s
message is encrypted with a public key, then only the associ- network boundaries are secure from cyberattack or intrusion,
ated private key can decrypt the message (and vice versa). If, and that if the organization’s boundaries are compromised,
for example, a person wants to send a purchase order to a the intrusion is detected quickly and combated.
vendor and have the contents remain private, the sender
encrypts the message with the buyer’s public key. When the Firewalls
vendor, who is the only one able to read the purchase order,
receives the order, the vendor decrypts it with the associated Firewalls are barriers between an internal trusted network
private key. (or a PC) and the untrustworthy Internet. A firewall is
designed to prevent unauthorized access to and from private
The PKI Process: Digital Signatures and Certificate networks, such as intranets. Technically, a firewall is com-
Authorities posed of hardware and a software package that separates a
Digital signatures are the electronic equivalent of personal private computer network (e.g., your LAN) from a public
signatures on paper. They are difficult to forge since they network (the Internet). Firewalls are designed mainly to pro-
authenticate the identity of the sender that uses the public tect against any remote login, access by intruders via back-
key. Digital signatures are legally treated as signatures on doors, spam, and different types of malware (e.g., viruses or
paper. To see how a digital signature works, go to searchse- macros). Firewalls come in several shapes and formats. A
curity.techtarget.com/definition/digital-signature. popular defense system is a DMZ. The DMZ can be designed
in two different ways, using a single firewall or with dual
Certificate Authority firewalls. For intelligent firewalls, see Teo (2016).
Independent agencies called certificate authorities (CAs)
issue digital certificates or SSL certificates, which are elec- The Dual Firewall Architecture: The DMZ
tronic files that uniquely identify individuals and websites In the DMZ architecture (DMZ stands for demilitarized
and enable encrypted communication. The certificate con- zone), there are two firewalls between the Internet and the
tains personal information and other information related to internal users. One firewall is between the Internet and the
the public key and the encryption method, as well as a signed DMZ (border firewall) and another one is between the DMZ
hash of the certificate data. and the internal network (see Figure 10.9). All public servers
are placed in the DMZ (i.e., between the two firewalls). With
Secure Socket Layer this setup, it is possible to have firewall rules that allow
PKI systems are further secured with SSL—a protocol for trusted partners access to the public servers, but the interior
e-commerce. The PKI with SSL makes e-commerce very firewall can restrict all incoming connections.
secure but cumbersome for users. One of the major proto-
cols in use today is Secure Socket Layer (SSL). SSL has Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
been succeeded by Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is
based on SSL. For further details, see searchsecurity.tech- Suppose a company wants to establish a B2B application,
target.com/definition/Transport-Layer-Security-TLS. providing suppliers, partners, and others access not only to
In the next section, the focus is on the company’s digital data residing on its internal website, but also to data con-
perimeters—the networks. tained in other files (e.g., Word documents) or in legacy