Page 373 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 373
360 11 Electronic Commerce Payment Systems and Order Fulfillment
Payment
Gateway
2
Authorize? 4 Replenishment?
Merchant
1
Order Inventory
Pay
3 Product Sourcing 5 Warehousing
Customer Available
8 Receipt
9 Returns Handling
7 Shipment, 6 Pick, Quality Check,
Tracking Pack, Ship
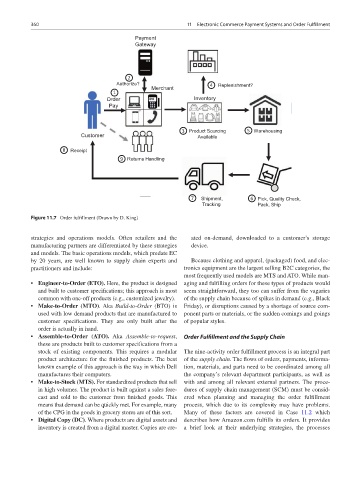
Figure 11.7 Order fulfillment (Drawn by D. King)
strategies and operations models. Often retailers and the ated on-demand, downloaded to a customer’s storage
manufacturing partners are differentiated by these strategies device.
and models. The basic operations models, which predate EC
by 20 years, are well known to supply chain experts and Because clothing and apparel, (packaged) food, and elec-
practitioners and include: tronics equipment are the largest selling B2C categories, the
most frequently used models are MTS and ATO. While man-
• Engineer-to-Order (ETO). Here, the product is designed aging and fulfilling orders for these types of products would
and built to customer specifications; this approach is most seem straightforward, they too can suffer from the vagaries
common with one-off products (e.g., customized jewelry). of the supply chain because of spikes in demand (e.g., Black
• Make-to-Order (MTO). Aka Build-to-Order (BTO) is Friday), or disruptions caused by a shortage of source com-
used with low demand products that are manufactured to ponent parts or materials, or the sudden comings and goings
customer specifications. They are only built after the of popular styles.
order is actually in hand.
• Assemble-to-Order (ATO). Aka Assemble-to-request, Order Fulfillment and the Supply Chain
these are products built to customer specifications from a
stock of existing components. This requires a modular The nine-activity order fulfillment process is an integral part
product architecture for the finished products. The best of the supply chain. The flows of orders, payments, informa-
known example of this approach is the way in which Dell tion, materials, and parts need to be coordinated among all
manufactures their computers. the company’s relevant department participants, as well as
• Make-to-Stock (MTS). For standardized products that sell with and among all relevant external partners. The proce-
in high volumes. The product is built against a sales fore- dures of supply chain management (SCM) must be consid-
cast and sold to the customer from finished goods. This ered when planning and managing the order fulfillment
means that demand can be quickly met. For example, many process, which due to its complexity may have problems.
of the CPG in the goods in grocery stores are of this sort. Many of these factors are covered in Case 11.2 which
• Digital Copy (DC). Where products are digital assets and describes how Amazon.com fulfills its orders. It provides
inventory is created from a digital master. Copies are cre- a brief look at their underlying strategies, the processes