Page 174 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 174
Exercises 159
transform lens is 100mm, what would be the allowable transversal
shift of the object?
2.36 An input transparency contains several 5 mm targets. If targets are to be
detected with the white light processor of Fig. 2.44,
(a) Calculate the required source size. Assume that the focal length of the
transform lenses is / = 500 mm.
(b) If the spatial frequency of the input object is assumed to be 10 lines
per millimeter, calculate the width of the spatial filter H n and the
required spatial frequency of the sampling phase grating.
2.37 Assume that the light source of Fig. 2.44 is a point source. If we ignore
the input signal transparency,
(a) Determine the smeared length of the Fourier spectra as a function of
the focal length / of the achromatic transform lens and the spatial
frequency p 0 of the sinusoidal phase grating T(x).
(b) If the spatial frequency of the diffraction grating is p 0 = 807i rad/mm
and / — 30 cm, compute the smeared length of the rainbow color
spectrum.
2.38 Referring to the preceding exercise, if the white light source is a uniformly
circular extended source of diameter D,
(a) Determine the size of the smeared Fourier spectra as a function of /
and p 0.
(b) If D = 2 mm, p 0 = 807i rad/mm, and / = 30 cm, determine the precise
size of the smeared Fourier spectra.
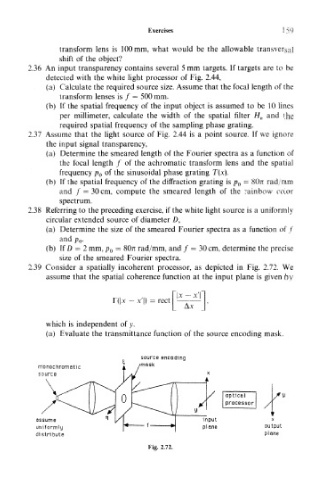
2.39 Consider a spatially incoherent processor, as depicted in Fig. 2.72. We
assume that the spatial coherence function at the input plane is given by
F(|.x rect
which is independent of y.
(a) Evaluate the transmittance function of the source encoding mask.
source encoding
monochromatic /mask
source
assume input X
uniformly plane output
distribute plane
Fig. 2.72.