Page 254 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 254
4.4. Optical Switching Based on MEMS
is the area of the plates. Corresponding to a voltage V applied to the capacitor.,
an electrostatic potential energy exists, given by
u (4.47)
This potential energy represents the energy required to prevent the opposite
charged parallel plates from collapsing into each other. The Coulumb force of
attraction is expressed as the negative gradient of the potential energy
F = -VL/.
Since
(4.49)
Then
F = (4.50)
2
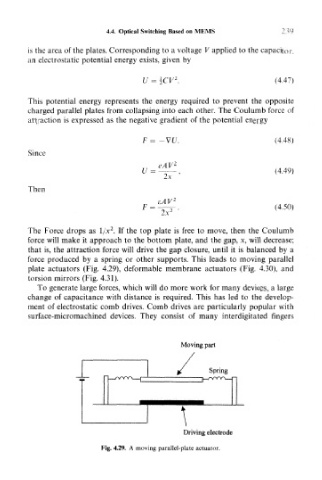
The Force drops as l/.x . If the top plate is free to move, then the Coulumb
force will make it approach to the bottom plate, and the gap, x, will decrease;
that is, the attraction force will drive the gap closure, until it is balanced by a
force produced by a spring or other supports. This leads to moving parallel
plate actuators (Fig. 4.29), deformable membrane actuators (Fig. 4.30), and
torsion mirrors (Fig. 4.31).
To generate large forces, which will do more work for many devices, a large
change of capacitance with distance is required. This has led to the develop-
ment of electrostatic comb drives. Comb drives are particularly popular with
surface-micromachined devices. They consist of many interdigitated fingers
Moving part
Spring
\
Driving electrode
Fig. 4.29. A moving parallel-plate actuator.