Page 588 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 588
10.2. A Brief Review of Types of Fiber-Optie Sensors !>73
10.2.1.1. Intensity-Type Fiber-Optic Sensors Using
Microbending
When a fiber is bent, there may be losses due to this bending. This localized
bending is called microbending. The output light intensity is proportional to
the amount of microbending. Therefore, by detecting changes in output light
intensity, the amount of microbending can be measured so a fiber-optic sensor
can be used.
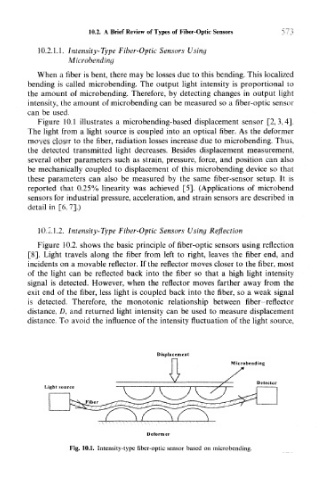
Figure 10.1 illustrates a microbending-based displacement sensor [2,3,4].
The light from a light source is coupled into an optical fiber. As the deformer
moves closer to the fiber, radiation losses increase due to microbending. Thus,
the detected transmitted light decreases. Besides displacement measurement,
several other parameters such as strain, pressure, force, and position can also
be mechanically coupled to displacement of this microbending device so that
these parameters can also be measured by the same fiber-sensor setup. It is
reported that 0.25% linearity was achieved [5]. (Applications of microbend
sensors for industrial pressure, acceleration, and strain sensors are described in
detail in [6,7].)
10.2.1.2. Intensity-Type Fiber-Optic Sensors Using Reflection
Figure 10.2. shows the basic principle of fiber-optic sensors using reflection
[8]. Light travels along the fiber from left to right, leaves the fiber end, and
incidents on a movable reflector. If the reflector moves closer to the fiber, most
of the light can be reflected back into the fiber so that a high light intensity
signal is detected. However, when the reflector moves farther away from the
exit end of the fiber, less light is coupled back into the fiber, so a weak signal
is detected. Therefore, the monotonic relationship between fiber-reflector
distance, D, and returned light intensity can be used to measure displacement
distance. To avoid the influence of the intensity fluctuation of the light source.
Displacement
Microbending
Light source
Fig. 10.1. Intensity-type fiber-optic sensor based on microbending.