Page 88 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 88
2,2. Processing under Coherent and Incoherent Illumination
-*ol~
i "
" lx" i s -4-—^
Light source input plane Output plane
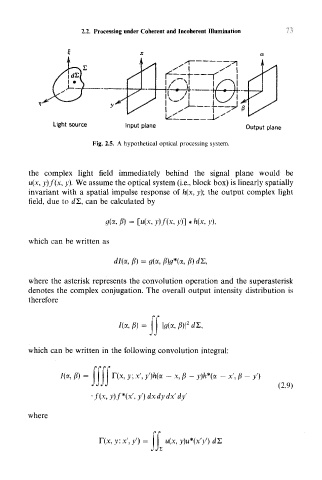
Fig. 2.5. A hypothetical optical processing system.
the complex light field immediately behind the signal plane would be
u(x, y)f(x, y). We assume the optical system (i.e., block box) is linearly spatially
invariant with a spatial impulse response of h(x, y); the output complex light
field, due to dZ, can be calculated by
which can be written as
where the asterisk represents the convolution operation and the superasterisk
denotes the complex conjugation. The overall output intensity distribution is
therefore
which can be written in the following convolution integral:
1
/(«, ft = T(x, y- x', y')h(a -x,0- y)h*(a -x ,?- y')
*/•/«/«/
(2.9)
• f(x, y)f*(x', y'} dx dy dx' dy'
where
x, y: x', y')= | u(x, y)u*(x'y')
li