Page 93 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 93
2. Signal Processing with Optics
A* y) g(<*, ffi
Fig. 2.7. Linear system representation.
complicated electronic spectrum analyzers or digital computers. However, this
complicated transform can be performed extremely simply with a coherent
optical system.
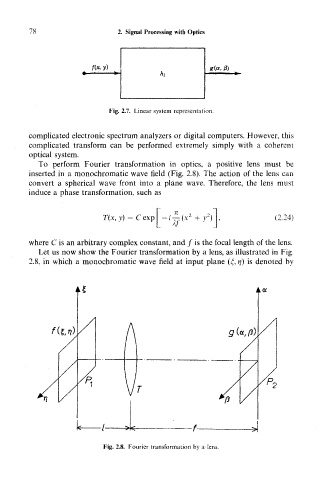
To perform Fourier transformation in optics, a positive lens must be
inserted in a monochromatic wave field (Fig. 2.8). The action of the lens can
convert a spherical wave front into a plane wave. Therefore, the lens must
induce a phase transformation, such as
T(x, y) = C exp (2.24)
where C is an arbitrary complex constant, and / is the focal length of the lens.
Let us now show the Fourier transformation by a lens, as illustrated in Fig.
2.8, in which a monochromatic wave field at input plane (£, rf) is denoted by
T
Fig. 2.8. Fourier transformation by a lens.