Page 95 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 95
80 2. Signal Processing with Optics
Fourier domain
.. i ^ y *v L filter H(p,q)
x
f
M ^
X
v / "A ^ s*t r\ X V
X X x X
X X VJ 1 \ s
XT U X
ViN
Input Fourier Output
plane plane
plane
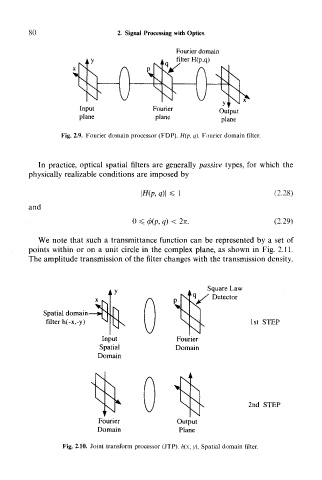
Fig. 2.9. Fourier domain processor (FDP). H(p, q), Fourier domain filter.
In practice, optical spatial filters are generally passive types, for which the
physically realizable conditions are imposed by
\H(p, q)\ < 1 (2,28)
and
0 < (t)(p, q) < 2n. (2.29)
We note that such a transmittance function can be represented by a set of
points within or on a unit circle in the complex plane, as shown in Fig. 2.11.
The amplitude transmission of the filter changes with the transmission density.
Square Law
^ °^./ Detector
Vh
Spatial domain—^>
filter h(-x,-y) ^ 1st STEP
Input Fourier
Spatial Domain
Domain
x X r\ > ^t [ X
x
x^ ^^ 1 1 k. X
\N \J ^ \ 2nd STEP
Fourier Output
Domain Plane
Fig. 2.10. Joint transform processor (JTP). h(x, y), Spatial domain filter.