Page 97 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 97
84 Boilers
Exhaust gas heat exchangers
The use of exhaust gases from diesel main propulsion engines to
generate steam is a means of heat energy recovery and improved plant
efficiency.
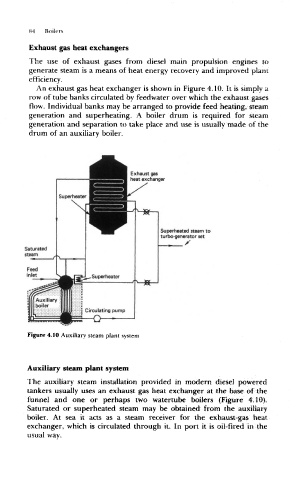
An exhaust gas heat exchanger is shown in Figure 4.10. It is simply a
row of tube banks circulated by feedwater over which the exhaust gases
flow. Individual banks may be arranged to provide feed heating, steam
generation and superheating. A boiler drum is required for steam
generation and separation to take place and use is usually made of the
drum of an auxiliary boiler.
Superheated steam to
turbo-generator set
Figure 4.10 Auxiliary steam plant system
Auxiliary steam plant system
The auxiliary steam installation provided in modern diesel powered
tankers usually uses an exhaust gas heat exchanger at the base of the
funnel and one or perhaps two watertube boilers (Figure 4.10).
Saturated or superheated steam may be obtained from the auxiliary
boiler. At sea it acts as a steam receiver for the exhaust-gas heat
exchanger, which is circulated through it. In port it is oil-fired in the
usual way.