Page 55 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 55
32 Chapter 2 The Instruction Set
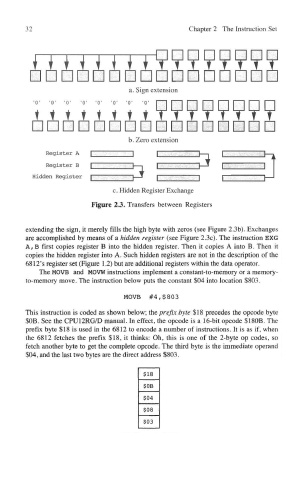
Figure 23. Transfers between Registers
extending the sign, it merely fills the high byte with zeros (see Figure 2.3b). Exchanges
are accomplished by means of a hidden register (see Figure 2.3c). The instruction EXG
A, B first copies register B into the hidden register. Then it copies A into B. Then it
copies the hidden register into A. Such hidden registers are not in the description of the
6812's register set (Figure 1.2) but are additional registers within the data operator.
The MOVB and MOVW instructions implement a constant-to-memory or a memory-
to-memory move. The instruction below puts the constant $04 into location $803,
MOVB #4,$803
This instruction is coded as shown below; the prefix byte $18 precedes the opcode byte
$OB. See the CPU12RG/D manual. In effect, the opcode is a 16-bit opcode $180B. The
prefix byte $18 is used in the 6812 to encode a number of instructions. It is as if, when
the 6812 fetches the prefix $18, it thinks: Oh, this is one of the 2-byte op codes, so
fetch another byte to get the complete opcode. The third byte is the immediate operand
$04, and the last two bytes are the direct address $803.