Page 60 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 60
2.2 Arithmetic Instructions 37
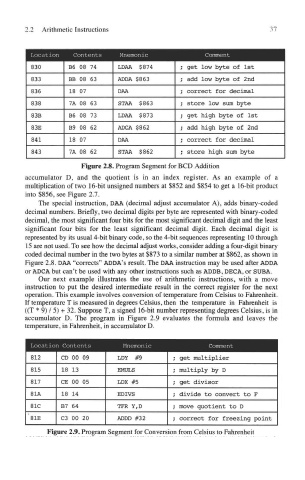
Figure 2.8. Program Segment for BCD Addition
accumulator D, and the quotient is in an index register. As an example of a
multiplication of two 16-bit unsigned numbers at $852 and $854 to get a 16-bit product
into $856, see Figure 2.7.
The special instruction, DAA (decimal adjust accumulator A), adds binary-coded
decimal numbers. Briefly, two decimal digits per byte are represented with binary-coded
decimal, the most significant four bits for the most significant decimal digit and the least
significant four bits for the least significant decimal digit. Each decimal digit is
represented by its usual 4-bit binary code, so the 4-bit sequences representing 10 through
15 are not used. To see how the decimal adjust works, consider adding a four-digit binary
coded decimal number in the two bytes at $873 to a similar number at $862, as shown in
Figure 2.8. DAA "corrects" ADDA's result. The DAA instruction may be used after ADDA
or ADCA but can't be used with any other instructions such as ADDB, DECA, or SUBA.
Our next example illustrates the use of arithmetic instructions, with a move
instruction to put the desired intermediate result in the correct register for the next
operation. This example involves conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
If temperature T is measured in degrees Celsius, then the temperature in Fahrenheit is
((T * 9) / 5) + 32. Suppose T, a signed 16-bit number representing degrees Celsius, is in
accumulator D. The program in Figure 2.9 evaluates the formula and leaves the
temperature, in Fahrenheit, in accumulator D.
Figure 2.9. Program Segment for Conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit