Page 62 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 62
2,3 Logic Instructions 39
Table 2.6. Logic Instructions
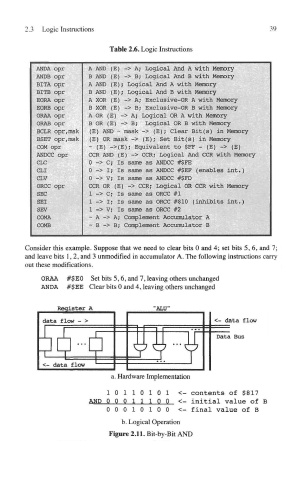
Consider this example. Suppose that we need to clear bits 0 and 4; set bits 5,6, and 7;
and leave bits 1,2, and 3 unmodified in accumulator A. The following instructions carry
out these modifications.
ORAA #$EO Set bits 5,6, and 7, leaving others unchanged
ANDA #$EE Clear bits 0 and 4, leaving others unchanged
1011010 1 <- contents of $817
AND 0001110 0 <- initial value of B
0001010 0 <- final value of B
b. Logical Operation
Figure 2.11. Bit-by-Bit AND