Page 102 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 102
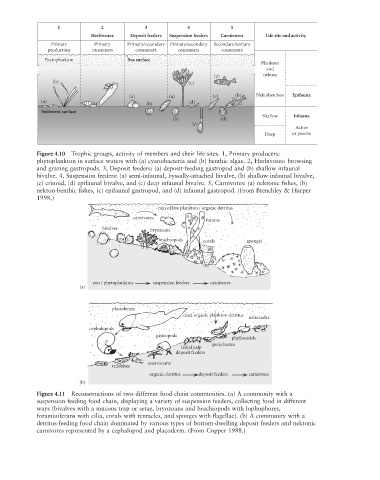
1 2 3 4 5
Herbivores Deposit feeders Suspension feeders Carnivores Life site and activity
Primary Primary Primary/secondary Primary/secondary Secondary/tertiary
production consumers consumers consumers consumers
Phytoplankton Sea surface
Plankton
and
(a) nekton
(b) (c)
(a) (a) (c) (b) Nektobenthos Epifauna
(a) (d)
(b)
Sediment surface
Shallow Infauna
(b) (d)
(e)
Active
Deep or passive
Figure 4.10 Trophic groups, activity of members and their life sites. 1, Primary producers:
phytoplankton in surface waters with (a) cyanobacteria and (b) benthic algae. 2, Herbivores: browsing
and grazing gastropods. 3, Deposit feeders: (a) deposit-feeding gastropod and (b) shallow infaunal
bivalve. 4, Suspension feeders: (a) semi-infaunal, byssally-attached bivalve, (b) shallow infaunal bivalve,
(c) crinoid, (d) epifaunal bivalve, and (e) deep infaunal bivalve. 5, Carnivores: (a) nektonic fi shes, (b)
nekton-benthic fishes, (c) epifaunal gastropod, and (d) infaunal gastropod. (From Brenchley & Harper
1998.)
rain of live plankton / organic detritus
carnivores
forams
bivalves
bryozoans
brachiopods corals sponges
zoo / phytoplankton suspension feeders carnivores
(a)
placoderms
dead organic plankton detritus
ostracodes
cephalopods
gastropods
phyllocarids
polychaetes
labial palp
deposit feeders
asterozoans
trilobites
organic detritus deposit feeders carnivores
(b)
Figure 4.11 Reconstructions of two different food chain communities. (a) A community with a
suspension-feeding food chain, displaying a variety of suspension feeders, collecting food in different
ways (bivalves with a mucous trap or setae, bryozoans and brachiopods with lophophores,
foraminiferans with cilia, corals with tentacles, and sponges with flagellae). (b) A community with a
detritus-feeding food chain dominated by various types of bottom-dwelling deposit feeders and nektonic
carnivores represented by a cephalopod and placoderm. (From Copper 1988.)