Page 124 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 124
110 PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
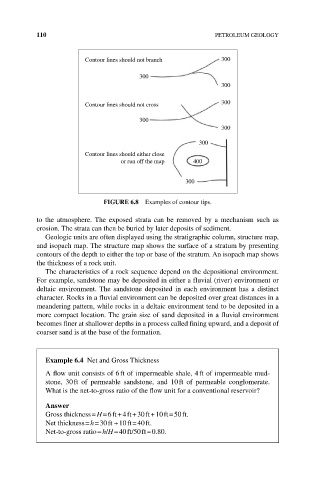
Contour lines should not branch 300
300
300
Contour lines should not cross 300
300
300
300
Contour lines should either close
or run off the map 400
300
FIGURE 6.8 Examples of contour tips.
to the atmosphere. The exposed strata can be removed by a mechanism such as
erosion. The strata can then be buried by later deposits of sediment.
Geologic units are often displayed using the stratigraphic column, structure map,
and isopach map. The structure map shows the surface of a stratum by presenting
contours of the depth to either the top or base of the stratum. An isopach map shows
the thickness of a rock unit.
The characteristics of a rock sequence depend on the depositional environment.
For example, sandstone may be deposited in either a fluvial (river) environment or
deltaic environment. The sandstone deposited in each environment has a distinct
character. Rocks in a fluvial environment can be deposited over great distances in a
meandering pattern, while rocks in a deltaic environment tend to be deposited in a
more compact location. The grain size of sand deposited in a fluvial environment
becomes finer at shallower depths in a process called fining upward, and a deposit of
coarser sand is at the base of the formation.
Example 6.4 Net and Gross Thickness
A flow unit consists of 6 ft of impermeable shale, 4 ft of impermeable mud-
stone, 30 ft of permeable sandstone, and 10 ft of permeable conglomerate.
What is the net‐to‐gross ratio of the flow unit for a conventional reservoir?
Answer
Gross thickness = H = 6 ft + 4 ft + 30 ft + 10 ft = 50 ft.
Net thickness = h = 30 ft + 10 ft = 40 ft.
Net‐to‐gross ratio = h/H = 40 ft/50 ft = 0.80.