Page 126 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 126
112 PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
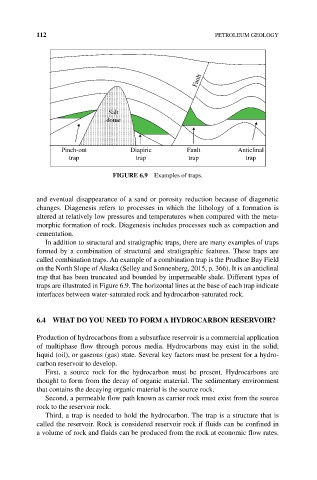
Fault
Salt
dome
Pinch-out Diapiric Fault Anticlinal
trap trap trap trap
FIGURE 6.9 Examples of traps.
and eventual disappearance of a sand or porosity reduction because of diagenetic
changes. Diagenesis refers to processes in which the lithology of a formation is
altered at relatively low pressures and temperatures when compared with the meta-
morphic formation of rock. Diagenesis includes processes such as compaction and
cementation.
In addition to structural and stratigraphic traps, there are many examples of traps
formed by a combination of structural and stratigraphic features. These traps are
called combination traps. An example of a combination trap is the Prudhoe Bay Field
on the North Slope of Alaska (Selley and Sonnenberg, 2015, p. 366). It is an anticlinal
trap that has been truncated and bounded by impermeable shale. Different types of
traps are illustrated in Figure 6.9. The horizontal lines at the base of each trap indicate
interfaces between water‐saturated rock and hydrocarbon‐saturated rock.
6.4 WHAT DO YOU NEED TO FORM A HYDROCARBON RESERVOIR?
Production of hydrocarbons from a subsurface reservoir is a commercial application
of multiphase flow through porous media. Hydrocarbons may exist in the solid,
liquid (oil), or gaseous (gas) state. Several key factors must be present for a hydro-
carbon reservoir to develop.
First, a source rock for the hydrocarbon must be present. Hydrocarbons are
thought to form from the decay of organic material. The sedimentary environment
that contains the decaying organic material is the source rock.
Second, a permeable flow path known as carrier rock must exist from the source
rock to the reservoir rock.
Third, a trap is needed to hold the hydrocarbon. The trap is a structure that is
called the reservoir. Rock is considered reservoir rock if fluids can be confined in
a volume of rock and fluids can be produced from the rock at economic flow rates.