Page 65 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 65
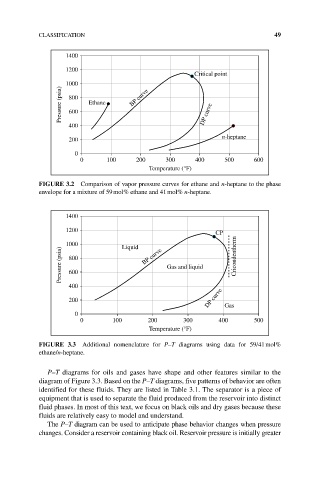
CLASSIFICATION 49
1400
1200
Critical point
1000
Pressure (psia) 800 Ethane BP curve DP curve
600
400
200 n-heptane
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Temperature (°F)
FIGURE 3.2 Comparison of vapor pressure curves for ethane and n‐heptane to the phase
envelope for a mixture of 59 mol% ethane and 41 mol% n‐heptane.
1400
1200 CP
Pressure (psia) 1000 Liquid BP curve Gas and liquid Cricondentherm
800
600
400
DP curve
200 Gas
0
0 100 200 300 400 500
Temperature (°F)
FIGURE 3.3 Additional nomenclature for P–T diagrams using data for 59/41 mol%
ethane/n‐heptane.
P–T diagrams for oils and gases have shape and other features similar to the
diagram of Figure 3.3. Based on the P–T diagrams, five patterns of behavior are often
identified for these fluids. They are listed in Table 3.1. The separator is a piece of
equipment that is used to separate the fluid produced from the reservoir into distinct
fluid phases. In most of this text, we focus on black oils and dry gases because these
fluids are relatively easy to model and understand.
The P–T diagram can be used to anticipate phase behavior changes when pressure
changes. Consider a reservoir containing black oil. Reservoir pressure is initially greater