Page 198 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 198
180 Chapter 8: Catalysis and Catalytic Reactions
Figures 8.2(b) and (c) illustrate two important aspects of surface catalysis that distin-
guish it from molecular catalysis:
(1) A distribution of “sites” exists on surfaces. By contrast with homogeneous and/or
molecular catalysts in which all the sites are the same, the catalytic sites on solid
surfaces can have a distribution of reactivities. The metal crystallites (which are
the molecular catalytic entity) are of different sizes. They also have several dif-
ferent types of surface metal atoms available for catalytic reactions. The metal
atoms are in a hexagonal packing arrangement on one face, while other faces
consist of the metal atoms arranged in a square pattern. The bonding of reaction
intermediates to these two surfaces is different. Further variety can be found
by considering the atoms at the edges between the various faces. Finally, as dis-
cussed in Chapter 6, bonding of an intermediate to a site can be influenced by
the bonding to nearby intermediates. Reaction mechanisms on surfaces are not
usually known in sufficient detail to discriminate among these possibilities. Nev-
ertheless, the simplifying assumption that a single type of site exists is often made
despite the fact that the situation is more complex.
(2) Intermediates on adjacent sites can interact because of the extended nature of
the surface. This option is not available to the isolated molecular catalytic entities.
This allows more possibilities for reactions between intermediates.
0 Gas phase intermediates
III H2 H H
c
r --------. H. 7 ,”
I ‘\
\ C ‘2
: \ \ d ‘H H2 H H
I \ \
I \ 9
I ‘. -.--_- ---,
I
\
I \
Energy \ \
I \
4 0 0 kJ mol-l \ \
\
I
0 I \ \ HHH
\p
III Hz H2 ; \
C , \ \
i \ b
I \
/ \
\ ---/ H
/ --\ ,.
\ /I Lb-,’ ’ \ / I
\ /---/ \--A
\ / H
0 I HHH
III H2 H2 : : OH o-C//H H H H \p
Pd Pd Pd Pd C \ / ic’ LlA!L \p
L--
-A’
H H H
I
Pd , Pd I , Pd Pd Pd I b
Pd Pd Pd Pd Pd \
Pd Pd Pd Pd Pd iL..-k H
Pd Pd Pd
P Pd Pd Pd
Reaction coordinate A 2-.E-u
Pd Pd Pd Pd Pd
Proposed catalytic intermediates
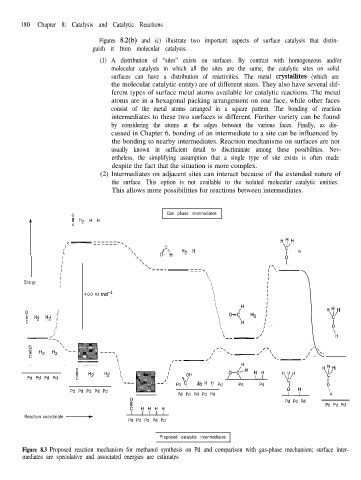
Figure 8.3 Proposed reaction mechanism for methanol synthesis on Pd and comparison with gas-phase mechanism; surface inter-
mediates are speculative and associated energies are estimates