Page 21 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 21
1.4 Aspects of Kinetics 3
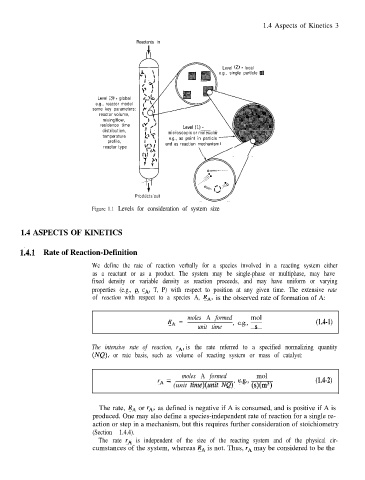
Reactants in
Level (2) - local
e.g., single particle
Level (3) - global
e.g., reactor model
some key parameters:
reactor volume,
mixing/flow,
residence time
distribution, microscopic or molecular
temperature e.g., as point in particle
profile, and as reaction mechanism
reactor type
\//
Products out
Figure 1.1 Levels for consideration of system size
1.4 ASPECTS OF KINETICS
1.4.1 Rate of Reaction-Definition
We define the rate of reaction verbally for a species involved in a reacting system either
as a reactant or as a product. The system may be single-phase or multiphase, may have
fixed density or variable density as reaction proceeds, and may have uniform or varying
properties (e.g., p, cA, T, P) with respect to position at any given time. The extensive rate
of reaction with respect to a species A, R,, is the observed rate of formation of A:
moles A formed mol
R, = , e.g., s (1.4-1)
unit time
The intensive rate of reaction, rA, is the rate referred to a specified normalizing quantity
(NQ), or rate basis, such as volume of reacting system or mass of catalyst:
moles A formed mol (1.4-2)
rA = (unit time)(unit NQ) e’g.’ (s)(m3)
The rate, RA or rA, as defined is negative if A is consumed, and is positive if A is
produced. One may also define a species-independent rate of reaction for a single re-
action or step in a mechanism, but this requires further consideration of stoichiometry
(Section 1.4.4).
The rate r, is independent of the size of the reacting system and of the physical cir-
cumstances of the system, whereas RA is not. Thus, rA may be considered to be the